
FINAL DAY VIR-X SALE: QUERCETIN and CANCER - New research of the past 4 years - 5 papers reviewed
Today is the last day to take advantage of the 20% OFF SALE and stock up on VIR-X, Ivermectin, Fenbendazole, Doxycyline and organic full spectrum CBD oil by using code V20
Papers reviewed
(2020, Jan, Tang et al) - Pharmacological basis and new insights of quercetin action in respect to its anti-cancer effects
(2022 Mar, Neamtu et al) - A Comprehensive View on the Quercetin Impact on Colorectal Cancer
(2022 Aug, Asgharian et al) - Potential mechanisms of quercetin in cancer prevention: focus on cellular and molecular targets
(2022 Oct, Biswa et al) - A Comprehensive Analysis and Anti-Cancer Activities of Quercetin in ROS-Mediated Cancer and Cancer Stem Cells
(2023, Feb, Maugeri et al) - Targets Involved in the Anti-Cancer Activity of Quercetin in Breast, Colorectal and Liver Neoplasms
======
(2020, Jan, Tang et al) - Pharmacological basis and new insights of quercetin action in respect to its anti-cancer effects (China)
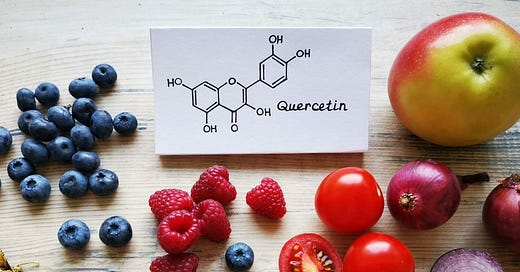
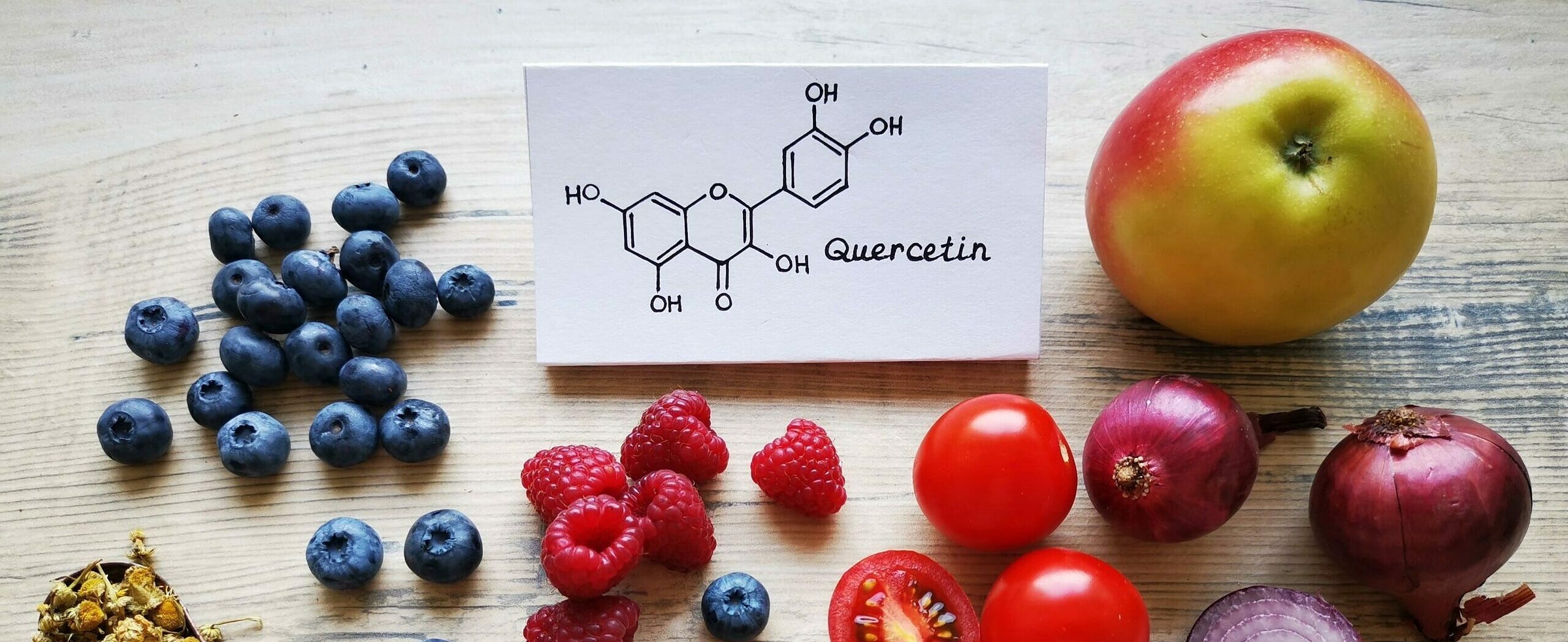
Quercetin is a flavonoid found in a variety of plants, fruits and vegetables such as onion, buckwheat and broccoli
Quercetin has recently been confirmed to have biological functions: anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant and anti-cancer
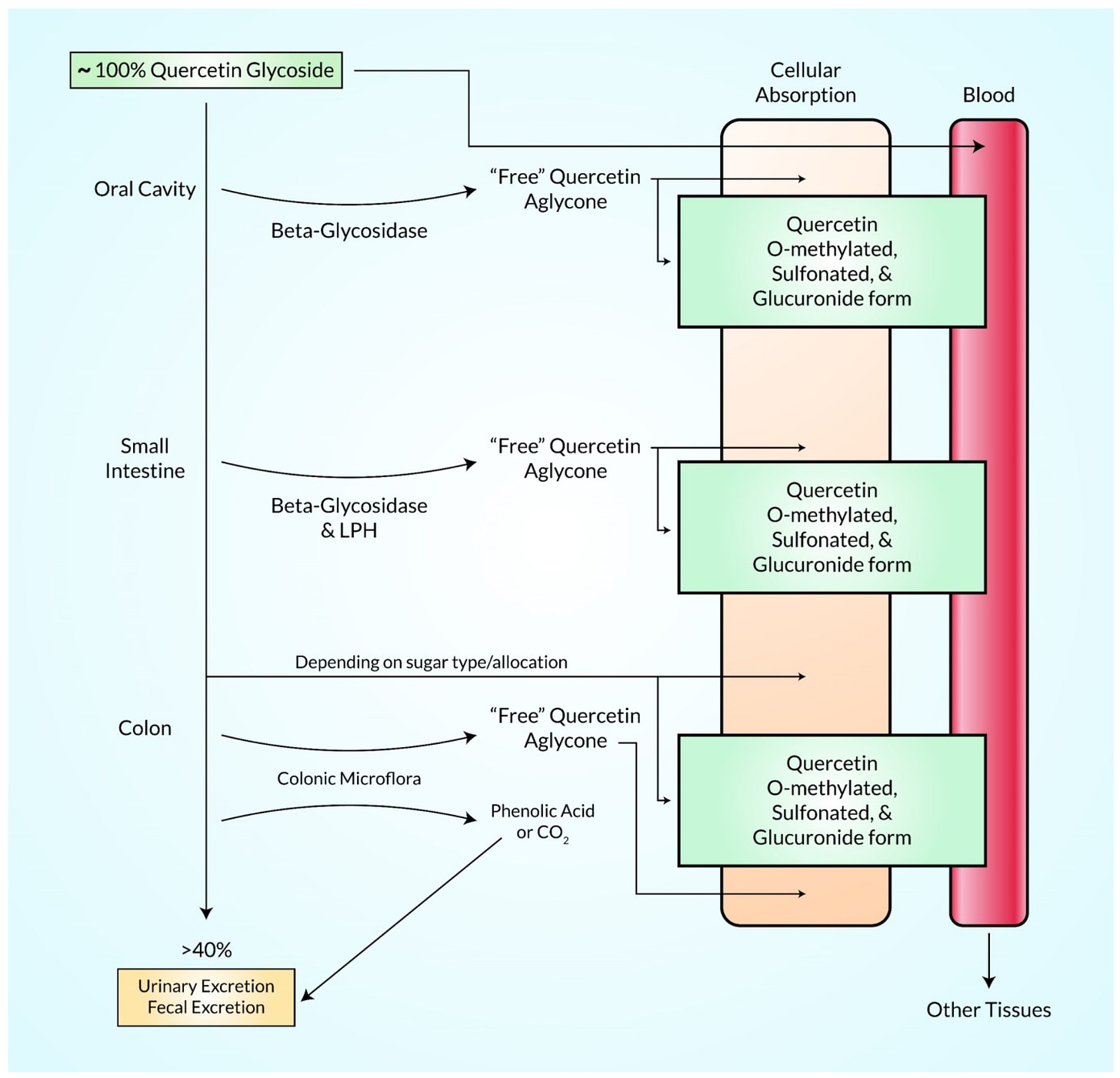
Quercetin is mainly absorbed into intestinal cells in the form of glycosides, hydrolyzed into aglycone and enters the intestinal lumen, and its mechanism may be related to glucose transport. The transformation process occurs mainly in the intestines, and some can be done in the liver and blood
Quercetin and its metabolites are mostly excreted in the intestine, and a small portion can be excreted in the urine by the kidneys
latest research: gut microbiota play an important role in generating glycosidases and enzymes, which can transfer quercetin into smaller, more easily absorbed molecules
Quercetin regulates iron metabolism - vital process - can quench iron catalyzed ROS production
antioxidant - Quercetin is an effective ROS scavenger, and inhibits lipid peroxidation
anti-inflammatory - inhibits release of inflammatory cytokines
anti-cancer:
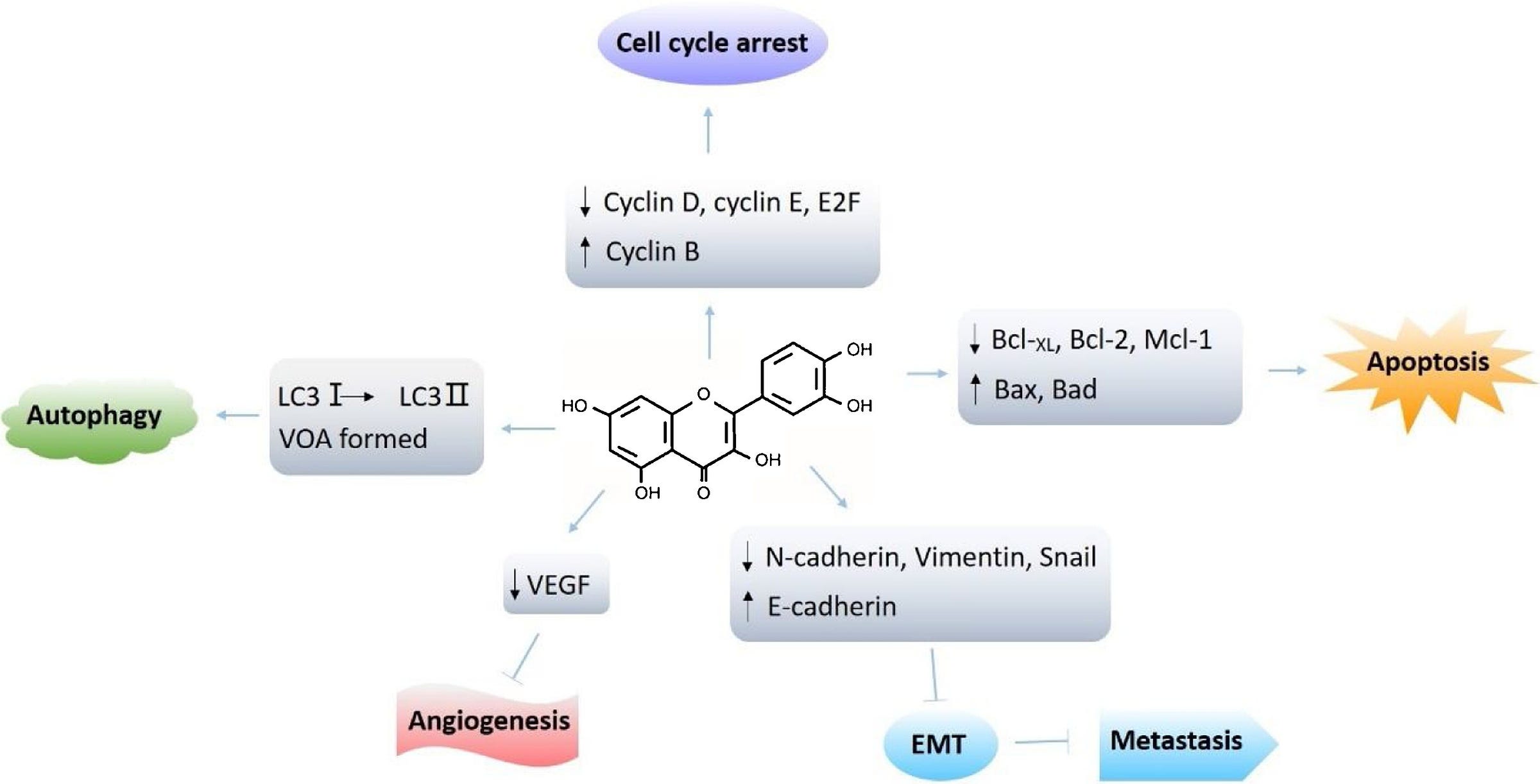
Quercetin induces cell cycle arrest, apoptosis, autophagy, inhibits angiogenesis and inhibits metastasis
Cell cycle arrest; breast cancer, prostate cancer, ovarian, gastric, osteosarcoma, CLL leukemia, lymphoma
apoptosis: lung colon, glioma, leukemia, gastric, ovarian, melanoma
anti-metastatic: colorectal, pancreatic, melanoma, head and neck
autophagy: glioblastoma, gastric, colon
Quercetin increases p53 expression (2008 Choi et al, 2010 Chou et al)
Quercetin can induce apoptosis of CANCER STEM CELLS
In vivo mouse studies: breast, prostate, lung, colorectal, pancreatic, melanoma, leukemia, gastric, liver
Conclusion:
“As a natural product, quercetin is a flavonoid compound, and treated with a reasonable dose of quercetin is non-toxic and has various inhibitory effects on various ways of tumor formation.”
“A large number of in vivo and in vitro experiments have shown that quercetin has a strong role in promoting apoptosis, inhibiting metastasis, and its ability to regulate cell cycle and tumor angiogenesis. Quercetin can influence the development of tumor by regulating epigenetics, which can directly regulate the expression of miRNA and the level of DNA methylation to exert anti-cancer effect and enhance the sensitivity of tumor cells to chemotherapy”
======
(2022 Mar, Neamtu et al) - A Comprehensive View on the Quercetin Impact on Colorectal Cancer (Romania, Hungary)
70% of colorectal cancer patients have no hereditary germ-line mutations or family history of pathology, thus being termed sporadic CRC
Diet and environmental factors are to date considered solely responsible for the development of sporadic CRC
Quercetin is a plant pigment and secondary metabolite, a polyphenolic flavonoid phytochemical with a well-characterized antioxidant activity
average daily intake is 25mg due to consumption of major food sources such as onions, asparagus, and berries
Quercetin and Colorectal Cancer
decreases ROS (antioxidant), decreases inflammation
inhibits cancer cell proliferation and growth, cell cycle arrest, apoptosis, inhibits metastasis
pathways involved: PI3K/AKT/mTOR, MAPK/Erk, MAPK/JNK, MAPK/p38, p-53, and NF-κB
(2006 Cruz-Correa et al) - 5 patients with prior colectomy and familial adenomatous polyposis had 6 month regimen of 60mg quercetin and 1.44g curcumin per day and had reduction in # and size of adenomatous polyps
Conclusion:
“Quercetin, a plant polyphenol abundantly found in many vegetables and fruits, up- and downregulates relevant pathways in the context of CRC, such as Wnt/β-catenin, PI3K/AKT/mTOR, MAPK/Erk, MAPK/JNK, MAPK/p38, p-53, and NF-κB signalling cascades. Due to its multitude of induced and/or inhibited molecular targets assessed both in vivo and in vitro, the functions of quercetin in pathological conditions, such as CRC, could be worth studying since certain anti-cancer effects are prominent.”
======
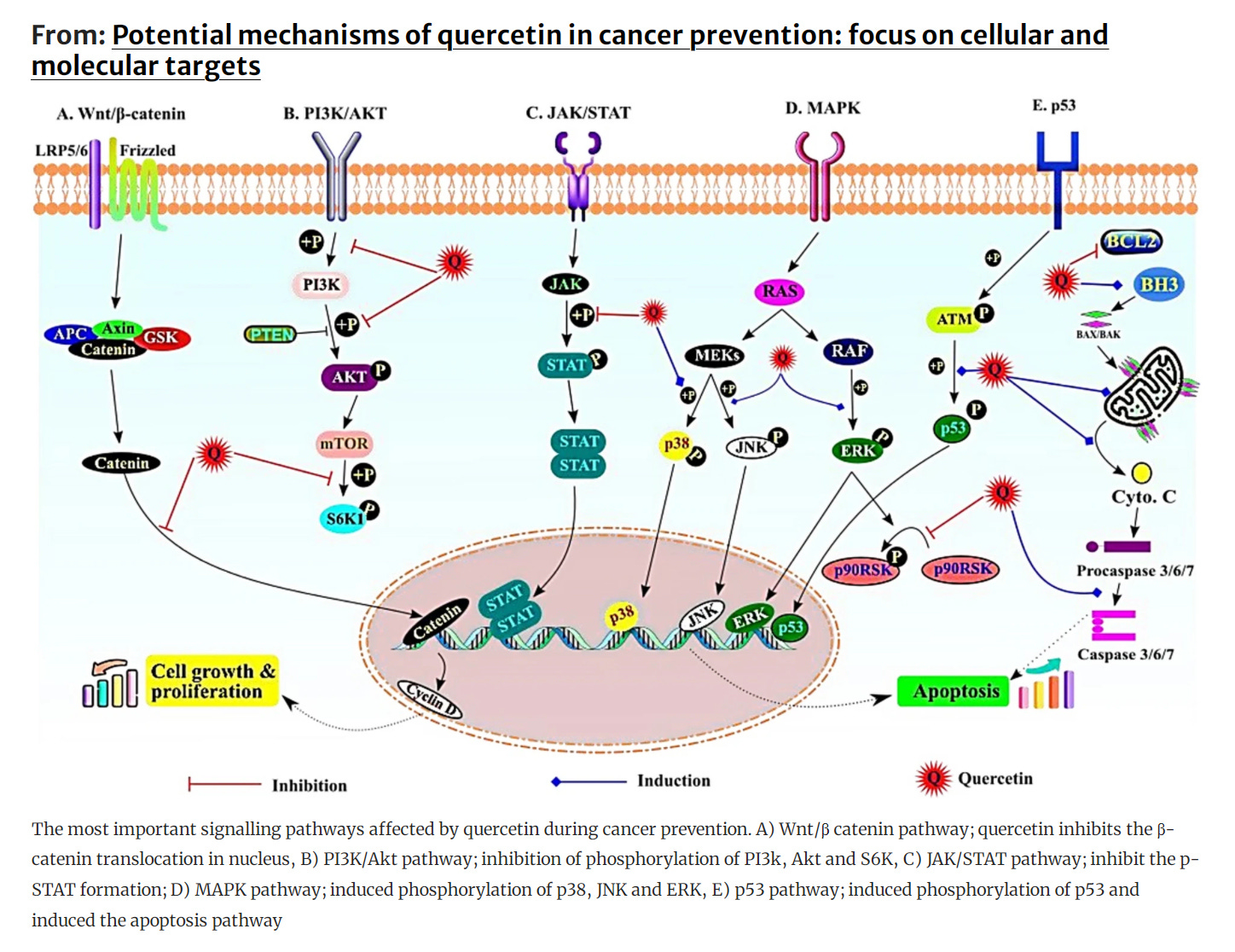
(2022 Aug, Asgharian et al) - Potential mechanisms of quercetin in cancer prevention: focus on cellular and molecular targets (Hong Kong)
Wnt/β-catenin pathway - involved in cell proliferation, differentiation, stemness, migration and apoptosis
PI3K/AKT pathway - cell cycle progression, differentiation, cell survival, and cell proliferation, apoptosis
JAK/STAT signalling pathway - cell division and growth, cell death, and tumor formation (cell cycle arrest)
MAPK signalling pathway - Cell proliferation, differentiation, gene expression, cell survival, mitosis, and apoptosis
p53, NF-ĸB, and apoptotic pathways - cell cycle arrest, apoptosis
Quercetin + Radiation - Pretreatment with quercetin could make ovarian cancer cells susceptible to radiation-induced cell death in p53 dependent manner, treatment of irradiation and quercetin could exacerbate DNA damages, cause apoptotic cell death
Quercetin + Tamoxifen - have been reported to control several apoptosis-related gene expressions including p53, Bax, p21, and Bcl-2 in breast cancer cells, leading to cell apoptosis regulation
Quercetin + gemcitabine or doxorubicin - Quercetin has been shown to enhance the efficacy of anti-cancer medications such as gemcitabine and doxorubicin, as measured by an increase in the proportion of dead cells
Quercetin + doxorubicin - use of quercetin may increase the anticancer effects of doxorubicin chemotherapy on liver cancer cells while protecting normal liver cells
Quercetin + temozolomide - The use of quercetin in combination with temozolomide, a standard care chemotherapy treatment for brain tumors, significantly improved the inhibitory effect of temozolomide on human glioblastoma/brain cancer cells and suppressed the survival of glioblastoma cells
Quercetin + cisplatin - studies done in human oral SCC cell lines and oral cancer in mice - combination of quercetin and cisplatin increased apoptosis in human oral cancer cells, as well as inhibited the growth of cancer in mice
Quercetin + hyperoside - synergic anticancer effects in prostate cancer, renal cancer
Quercetin + Resveratrol - had anti-cancer benefits in a mouse model of prostate cancer
Quercetin + green tea catechin - prevents progression of pancreatic cancer
Quercetin + arctigenin - in prostate cancer, can inhibit expression of oncogenic miRs
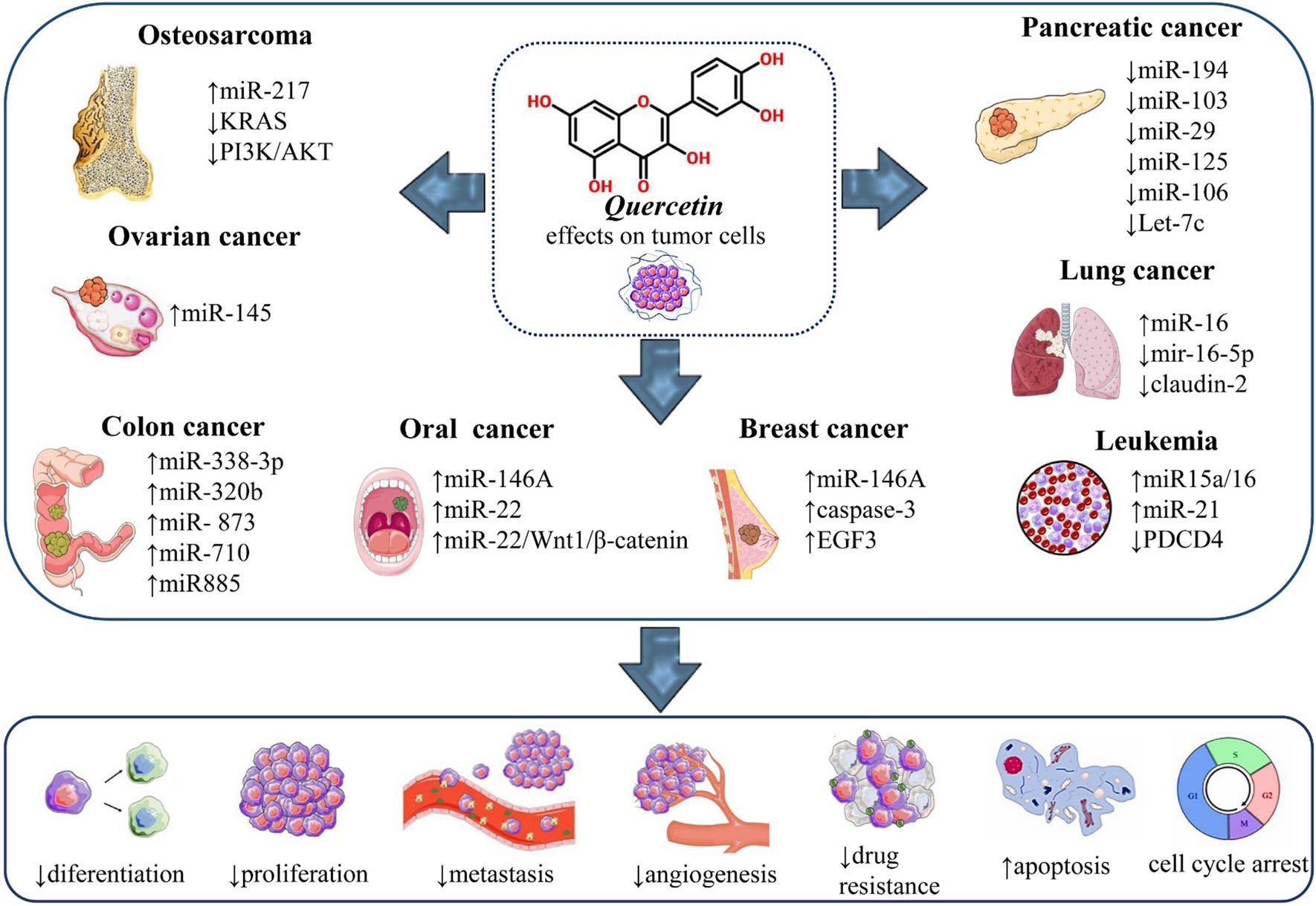
Epigenetic Modulation by Quercetin - Regulation of miRNAs in different cancer types: effects on cancer cell progression and proliferation
Part of the quercetin anticancer effect is exerted by regulating the expression of miRNAs (micro RNAs)
Cancer Prevention - in vivo studies have shown that quercetin is involved in the prevention of several types of cancer, especially colon cancer
Suppression of carcinogenesis may be due to its radical inhibitory activity and quercetin has been reported to reduce the CYP450 family of enzymes, which plays a key role in the activation of several suspected human carcinogens.
Quercetin + p53 - Quercetin increases the stability of and promotes the apoptotic effects of the p53 gene through quercetin's ability to phosphorylate and stabilize the p53 gene.
CONCLUSION:
“Quercetin possesses some significant anticancer activities. It has been shown that quercetin uses multiple mechanisms to exert its anticancer effects by modulating different dysregulated signalling pathways which implicated apoptosis and autophagy”
“there is an urgent need for different in vivo studies in this field to analyze the therapeutic activities and safety of quercetins.”
“Among natural plant extracts, quercetin shows several significant biological anti-tumor effects. ncRNA (non-coding RNA including miRNA and lncRNA long non-coding RNA) plays a key role in cancer development. Quercetin regulates the expression of ncRNAs, which in turn affects the related signalling pathway genes/proteins expression, suppresses the cancer cell growth, promotes cell apoptosis, and enhances sensitivity to chemotherapy agents. Taken together, quercetin is a natural compound with a potential anticancer effect in the adjuvant treatment of cancers.”
======
(2022 Oct, Biswa et al) - A Comprehensive Analysis and Anti-Cancer Activities of Quercetin in ROS-Mediated Cancer and Cancer Stem Cells (Bangladesh)
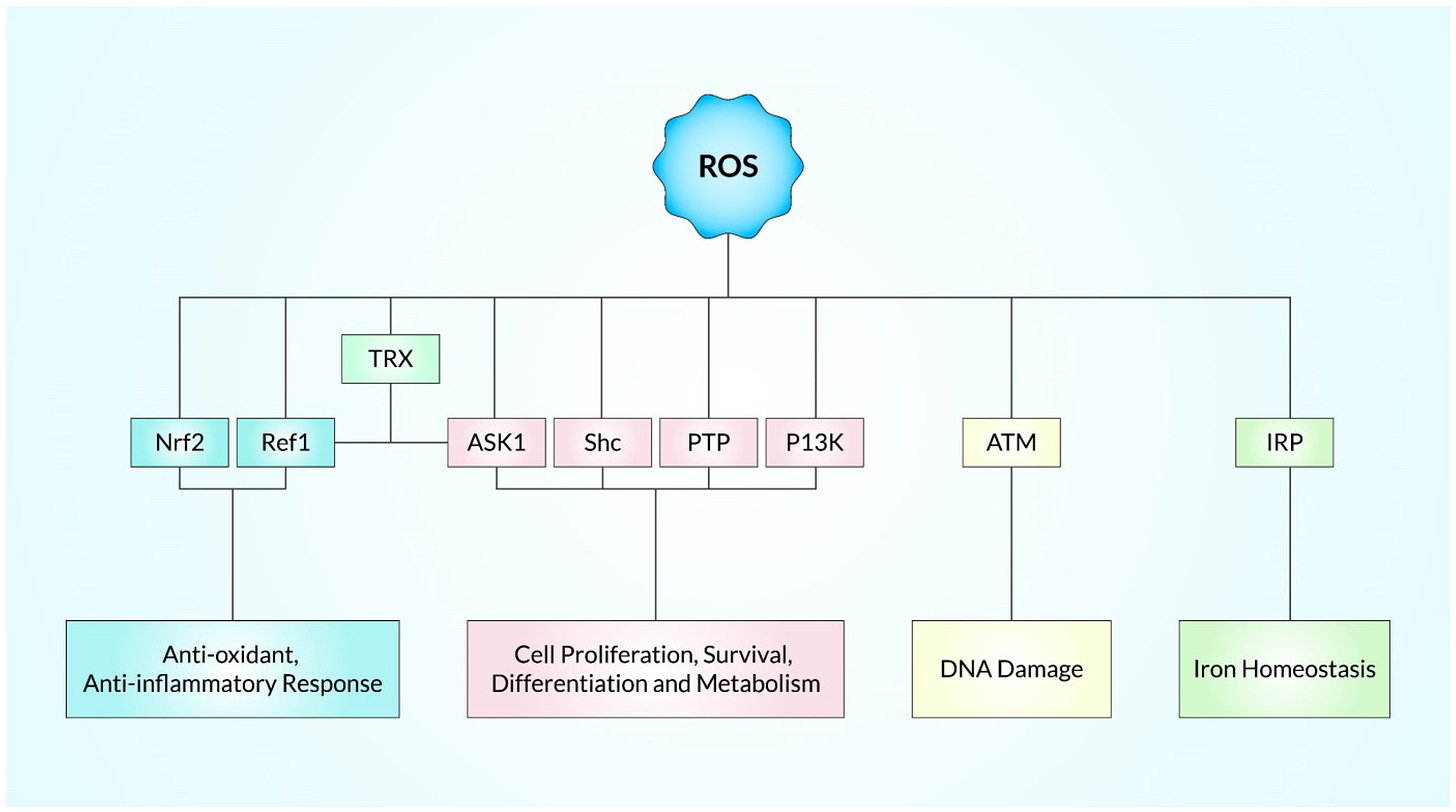
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) induce carcinogenesis by causing genetic mutations, activating oncogenes, and increasing oxidative stress, all of which affect cell proliferation, survival, and apoptosis.
When compared to normal cells, cancer cells have higher levels of ROS, and they are responsible for the maintenance of the cancer phenotype;
large amounts of ROS make cancer cells extremely susceptible to Quercetin
QC is lipophilic in nature and can easily pass through the cell membranes and latterly activate numerous intracellular signaling pathways
ROS are responsible for Quercetin mediated cell death in cancer
enhances p53 pathway:
Quercetin increases p53 phosphorylation, it does not increase p53 mRNA transcription.
prevention of p53 mRNA degradation at the post-transcriptional stage occurred through quercetin-mediated signaling
Inhibits JAK-STAT pathway - anti-inflammatory
Activates ASK1/AMPK/p38 pathway - apoptosis
Inhibits PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway - reduces breast cancer stem cells
Conclusion:
“QC has been shown to be safe with no documented side effects when used to treat human cancer. Given the numerous benefits associated with QC and its derivatives, it is high time to continue investigating these molecules’ effects on cancer prevention with treatment”
======
(2023, Feb, Maugeri et al) - Targets Involved in the Anti-Cancer Activity of Quercetin in Breast, Colorectal and Liver Neoplasms (Italy)
flavonoids are valuable allies for both cancer prevention and therapy
flavonoids have anti-oxidant and radical scavenging activities, inhibit cytokines via immune cell modulation, and alter adhesion molecules
Quercetin, flavonol abundant in a wide variety of plants, deserves to be considered the leading molecule of the whole flavonoid class
Breast cancer
Quercetin has been studied for decades in breast cancer
Quercetin increases ROS and induces apoptosis, increases tumor suppressor (PTEN)
Quercetin has synergistic effects with chemo (docetaxel, 5-FU)
Quercetin can overcome chemo drug resistance - could enhance the cytotoxic effect of doxorubicin, paclitaxel and vincristine by decreasing P-glycoprotein protein level
Colorectal cancer
Quercetin studied for CRC over 30 years
Quercetin’s exact mechanism of action is not understood
generates ROS and induces apoptosis, increases tumor suppressor (PTEN)
Quercetin + radiation = reduction in tumor volume
Quercetin + chemo (5-FU, cisplatin, doxorubicin) - enhanced cell death
CONCLUSION:
“Different phases of the carcinogenic process can be targeted by phytochemicals, and an increasing number of studies suggests that these compounds may be useful for both prevention and as co-adjuvants in anti-cancer therapy. This is because compared to synthetic drugs, their lower specificity is their forte since several targets can be simultaneously influenced by phytochemicals. Quercetin stands out among the other flavonoids given a plethora of its documented pharmacological activities, including anti-cancer one.”
======
My Take:
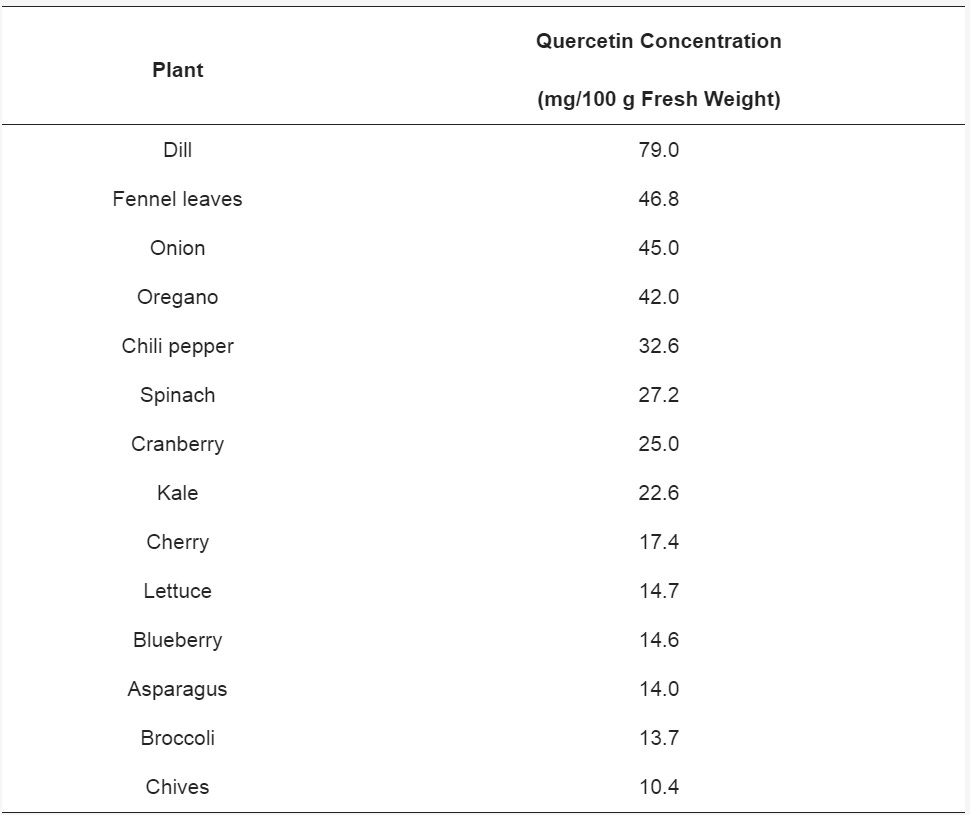
Quercetin is a flavonoid found in a variety of plants, highest concentrations in onions (45mg), oregano (42mg), buckwheat (36mg), spinach (27mg), cranberry (25mg), kale (23mg), cherries (17mg), blueberries (15mg), asparagus (14mg) per 100 grams.
Quercetin is an anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory and has anti-cancer properties.
In this article I reviewed 5 studies that were done in China, Hong Kong, Romania, Hungary, Italy and Bangladesh (none in USA, Canada, UK, Australia).
Quercetin, as an anti-oxidant is able to PREVENT certain cancers, mainly colorectal cancer.
Quercetin exerts anti-cancer properties mainly through regulation of ROS (reactive oxygen species) which affects numerous cellular signalling pathways, that ultimately result in cancer cell death via: apoptosis, cell cycle arrest, autophagy, inhibited angiogenesis, inhibited metastasis.
Quercetin stabilizes p53 and increases p53 levels which leads to cancer cell apoptosis.
Quercetin is able to induce apoptosis of CANCER STEM CELLS (which are responsible for metastases and recurrences).
Quercetin regulates microRNAs (miRs) which are implicated in many cancers and Quercetin exerts anti-cancer properties by enhancing tumor suppressor miRs and inhibiting oncogenic miRs.
Best studied cancers with Quercetin are breast cancer and colorectal cancer.
Quercetin in vivo mouse studies show anti-cancer effects in: breast, colorectal, liver, prostate, lung, pancreatic, melanoma, leukemia, gastric
Quercetin is synergistic with many other treatments:
Quercetin is synergistic with chemo and increases efficacy of cancer cell killing
Quercetin is synergistic with radiation therapy
Quercetin reverses chemo drug resistance
Quercetin is synergistic with bioactive compounds (resveratrol, green tea catechins EGCG)
If you’re adding Quercetin to your “Alternative Cancer Treatment” regimen, I highly recommend getting the most bioavailable version possible.
The above turbo cancer treatment plan should be combined with the following:
New & Improved Synergistic Joe Tippens Protocol
Tocotrienol and Tocopherol forms (all 8) of Vitamin E (400-800mg per day, 7 days a week). A product called Gamma E by Life Extension or Perfect E are both great.
Bio-Available Curcumin (600mg per day, 2 pills per day 7 days a week). A product called Theracurmin HP by Integrative Therapeutics is bioavailable.
Vitamin D (62.5 mcg [2500 IU] seven days a week).
CBD oil (1-2 droppers full [equal to 167 to 334 mg per day] under the tongue, 7 days a week) CBD-X: The most potent full spectrum organic CBD oil, with 5,000 milligrams of activated cannabinoids and hemp compounds CBD, CBN & CBG per serving.
Fenbendazole (300mg, 6 days a week) or in the case of severe turbo cancers up to 1 gram
Ivermectin (24mg, 7 days a week) or in the case of severe turbo cancers up to 1mg/kg/day
VIR-X immune support (2 capsules per day)
Sale ends today, July 14th, 2024: Upon adding products to your cart, please go to the cart icon at the top right corner of your browser page and click it, then choose the VIEW CART option whereby you will be redirected to a page where you can enter the code V20 in the Use Coupon Code field.
Please contact the company directly with any product questions: info@virex.health
They want you dead.
Do NOT comply.

















So how much quercetin to take for cancer prevention? I have personally witnessed improvements in seasonal and environmental allergies when taking 800 to 1000 mg. Is half that amount going to prevent cancer? Quercetin also reduces mast cells.
Going back on Quercetin now. My seasonal allergies have been crap since I stopped taking it.