
IVERMECTIN and CANCER, it has at least 15 anti-cancer mechanisms of action. Can Ivermectin Treat COVID-19 mRNA Vaccine Induced Turbo Cancers? - 9 Ivermectin papers reviewed
A critically important article that further reinforces this Substack’s thesis that Ivermectin may cure turbo cancers; for example:
Papers reviewed:
2023 Sep.23 - Man-Yuan Li et al - Ivermectin induces nonprotective autophagy by downregulating PAK1 and apoptosis in lungadenocarcinoma cells
2023 May - Samy et al - Eprinomectin: a derivative of ivermectin suppresses growth and metastatic phenotypes of prostate cancer cells by targeting the β-catenin signaling pathway
2022 Nov - Lotfalizadeh et al - The Anticancer potential of Ivermectin: Mechanisms of action and therapeutic implications
2022 Oct - Jian Liu et al - Progress in Understanding the Molecular Mechanisms Underlying the Antitumour Effects of Ivermectin
2022 Jun - Daeun Lee et al - Ivermectin suppresses pancreaticcancer via mitochondria dysfunction
2021 Aug - Shican Zhou et al - Ivermectin has New Application in Inhibiting Colorectal Cancer Cell Growth
2021 Jan - Mingyang Tang et al - Ivermectin, a potential anticancer drug derived from an antiparasitic drug
2019 Sep Intuyod et al - Anti-parasitic Drug Ivermectin Exhibits Potent Anticancer Activity Against Gemcitabine-resistant Cholangiocarcinoma In Vitro
2018 Feb - Juarez et al - The multitargeted drug ivermectin: from an antiparasitic agent to a repositioned cancer drug
2018 Feb - Juarez et al - The multitargeted drug ivermectin: from an antiparasitic agent to a repositioned cancer drug
Satoshi Omura at the Kitasato Institute discovered Ivermectin in 1979 and was awarded a Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for this discovery in 2015
Ivermectin was FDA Approved for human use in 1987 to orally treat onchocerciasis, also known as river blindness, caused by the blackfly-transmitted parasite Onchocerca volvulus
Ivermectin is annually taken by close to 250 million people
most patients treated with Ivermectin have no side-effects other than those caused by the immune and inflammatory responses against the parasite, such as fever, pruritus, skin rashes and malaise
maximum concentration in plasma is reached 4-5 h after its oral administration
its half-life is approximately 19 h and is metabolized in the liver by the cytochrome CYP1A and CYP3A4 complexes, generating 10 metabolites, mostly demethylated and hydroxylated.
Its excretion is mainly by feces and only 1% is excreted in the urine
Ivermectin exerts antitumor effects in different types of cancer.
What this means Clinically:
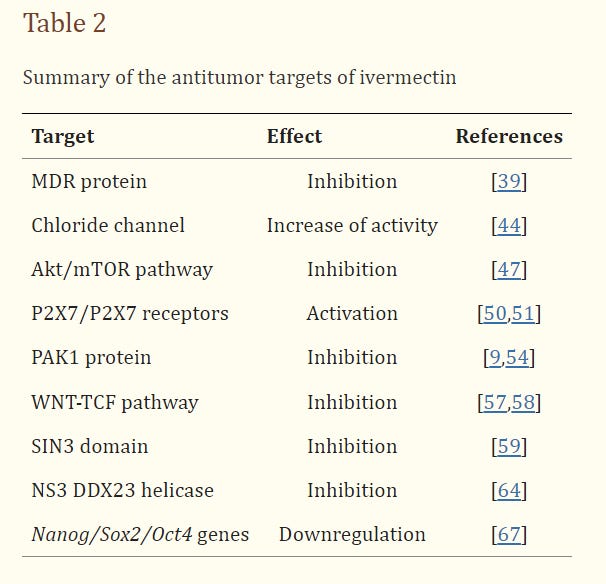
Chloride channel - Acute myeloid leukemia - induced cell death
Akt/mTOR path - glioblastoma, renal cancer cell lines - inhibition of mitochondrial biogenesis or function, oxidative stress, DNA damage
P2X7 (ICD) overexpression promotes tumor growth and metastases - ivermectin potentiates immunogenic cell death (ICD) in triple negative breast cancer cells
PAK1 (Autophagy) - glioblastoma and ovarian cancer cell lines - Ivermectin promotes autophagy through this pathway
WNT-TCF pathway - glioblastoma, colon cancer, melanoma - Ivermectin exerts anti-proliferative function through this pathway (possibilities to use Ivermectin to block WNT-TCF dependent cancers like breast, skin, lung)
SIN3 Domain - breast cancer (Ivermectin acts as epigenetic modulator to alter gene expression and decrease tumor growth)
NS3 helicase - glioma cells - Ivermectin had anti-tumor effects by acting as helicase inhibitor
In Vitro Studies:
breast cancer, ovarian, prostate, colon, pancreas, head and neck, melanoma - inhibits cell proliferation, induction of apoptosis, autophagy, reversion of tamoxifen resistance, inhibits metastases
glioblastoma - growth inhibition, apoptosis, and anti-angiogenesis
In Vivo Studies (done on immune deficient mice):
acute myeloblastic leukemia - reduce tumor volume up to 70%
glioblastoma - reduce tumor volume up to 50%
breast cancer - reduce tumor volume up to 60%
glioma - reduce tumor volume up to 50% (at 0.24mg/kg), however at human dose equivalent to 0.8mg/kg tumors were not detectable!
colon cancer - reduce tumor volume up to 85%
median dose employed was equivalent to 0.4 mg/kg in humans from 10 to 42 days (oral, intraperitoneal or intra-tumoral)
the in vitro and in vivo antitumor activities of Ivermectin are achieved at concentrations that can be clinically reachable based on the human pharmacokinetic studies done in healthy and parasited patients
2019 Sep Intuyod et al - Anti-parasitic Drug Ivermectin Exhibits Potent Anticancer Activity Against Gemcitabine-resistant Cholangiocarcinoma In Vitro
Ivermectin studied on cholangiocarcinoma cells that were chemo resistant (gemcitabine)
Ivermectin inhibited cancer cell proliferation and colony formation in a dose and time dependent manner(!)
Ivermectin caused S-phase cell cycle arrest and cell death
Conclusion: “Ivermectin might be useful as an alternative treatment for cholangiocarcinoma, especially in patients who do not respond to chemo.”
2021 Jan - Mingyang Tang et al - Ivermectin, a potential anticancer drug derived from an antiparasitic drug
specific mechanism of IVM-mediated cytotoxicity in tumor cells is unclear; it may be related to the effect of IVM on various signaling pathways
IVM seems to induce mixed cell death in tumor cells
CONCLUSIONS: Ivermectin selectively inhibits the proliferation of tumors at a dose that is not toxic to normal cells and can reverse the MDR (multi-drug resistance) of tumors.
In healthy volunteers, the dose was increased to 2 mg/kg, and no serious adverse reactions were found
Unfortunately, there have been no reports of clinical trials of IVM as an anticancer drug
large number of research results indicate that IVM affects multiple signaling pathways in tumor cells and inhibits proliferation, IVM may cause antitumor activity in tumor cells through specific targets
Ivermectin regulates the tumor microenvironment, inhibits the activity of tumor stem cells and reduces tumor angiogenesis and tumor metastasis.
It has become increasingly clear that Ivermectin can induce a mixed cell death mode involving apoptosis, autophagy and pyroptosisdepending on the cell conditions and cancer type.
Ivermectin can enhance the sensitivity of chemotherapeutic drugs and reduce the production of resistance. Therefore, IVM should be used in combination with other drugs to achieve the best effect
2022 Jun - Daeun Lee et al - Ivermectin suppresses pancreatic cancer via mitochondria dysfunction
Poster presentation from South Korea
Ivermectin was combined with gemcitabine in pancreatic cancer
Ivermectin-gemcitabine combination inhibited pancreatic cancer cell proliferation via G1 arrest of cell cycle
in vivo experiments showed ivermectin-gemcitabine significantly suppressed tumor growth of pancreatic cancer compared with gemcitabine alone
Conclusion: “Ivermectin could be a potential antitumor drug for the treatment of pancreatic cancer”
2021 Aug - Shican Zhou et al - Ivermectin has New Application in Inhibiting Colorectal Cancer Cell Growth
Colorectal cancer is 3rd most common cancer worldwide, lacks effective therapy
Ivermectin tested on colorectal cancer cell lines
Ivermectin dose-dependently inhibited colorectal cancer growth
promoted cell apoptosis
promoted total and mitochondrial ROS production (reactive oxygen species)
induced colorectal cancer cell S-phase arrest
Conclusion: Ivermectin might be a new potential anticancer drug therapy for human colorectal cancer
2022 Oct - Jian Liu et al - Progress in Understanding the Molecular Mechanisms Underlying the Antitumor Effects of Ivermectin
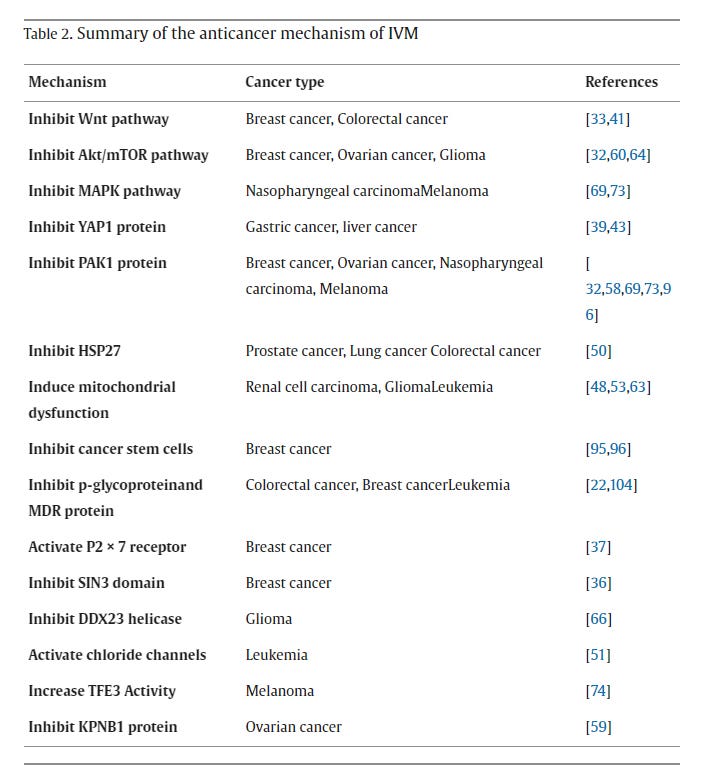
PAK1 (Autophagy) - Ivermectin, acts as PAK1 inhibitor and inhibits growth of breast cancer, ovarian cancer, glioblastoma and NF2tumors and involved in cell death in Nasopharyngeal carcinoma and melanoma.
Apoptosis (Caspase Dependent) - Ivermectin induces apoptosis in glioblastoma, chronic myeloid leukemia cells, also breast cancer, ovarian cancer.
Immunogenic Cell Death (ICD - P2X7 signaling) - ivermectin induces cell death in triple negative breast cancer.
YAP1 Inhibition - hepatocellular and cholangiocarcinoma, colorectal cancer, ovarian cancer, gastric cancer - ivermectin exerts anti-tumor effects
WNT Path (cancer progression - differentiation, metastasis, cell senescence, tumor initiation, tumor growth) - Ivermectin inhibits this path - inhibits colon cancer and lung cancer, ivermectin also limits formation of cancer stem cells.
TF3 Path - ivermectin stimulates apoptosis of melanoma cells.
RNA Helicase Inhibition - ivermectin inhibits cell invasion and proliferation of glioma cells
SID Peptide (SIN3A/B) - Ivermectin inhibits breast cancer progression, also restores tamoxifen sensitivity
Akt/mTOR inhibition - Ivermectin inhibits mitochondrial respiration - glioblastoma, CML leukemia (some cancers like breast, leukemia and lymphoma are more metabolically active and depended on mitochondria - more responsive to ivermectin inhibition)
ivermectin is an angiogenesis inhibitor
ivermectin has anti-mitotic activity
In humans, toxicity of ivermectin is very low, no serious adverse reactions have been found in healthy volunteers at dose up to 120 mg (~2 mg/kg) (Reference: GuzzoCA, FurtekCI, PorrasAG, et al. Safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of escalating high doses of ivermectin in healthy adult subjects. J Clin Pharmacol. 2002;42(10):1122–1133.)
2023 May - Samy et al - Eprinomectin: a derivative of ivermectin suppresses growth and metastatic phenotypes of prostate cancer cells by targeting the β-catenin signaling pathway
Ivermectin (derivative) inhibits prostate cancer cell viability, migration capacities
Ivermectin induces apoptosis, autophagy (via ROS)
Ivermectin downregulates expression of cancer stem cell markers
Conclusion: Ivermectin has tremendous potential to target metastatic prostate cancer cells and provides new avenues for therapeutic approaches to advanced prostate cancer
2023 Sep.23 - Man-Yuan Li et al - Ivermectin induces nonprotective autophagy by downregulating PAK1 and apoptosis in lung adenocarcinoma cells
Ivermectin was studied on lung adenocarcinoma cells
Ivermectin strikingly impeded colony formation and viability of cancer cells, along with cell proliferation, caused apoptosis and enhanced autophagy
Ivermectin efficiently suppressed cellular growth of lung adenocarcinoma cells in vivo among nude mice
My Take…
Ivermectin exerts anti-cancer effects through at least 15 different pathways proven in the medical literature, both in vitro and in vivo!
(You get a nice summary of these 15 pathways from the 2021 paper byMingyang Tang et al.)
First, let’s quickly summarize the anti-cancer mechanisms (a quick summary can be found in 2022 paper by Loftalizadeh et al):
Ivermectin induces tumor cell death: apoptosis, autophagy, pyroptosis
Ivermectin inhibits tumor initiation and tumor progression (via WNT inhibition, YAP1 inhibition)
Ivermectin inhibits tumor growth and proliferation (via Akt/mTOR inhibition, MAPK inhibition)
Ivermectin stops cancer cell migration, invasion and metastasis (via PAK1 inhibition - seen in 70% of all cancers, EMT inhibition, RNA Helicase inhibition)
Ivermectin causes cancer cell mitochondrial dysfunction (inhibits mitochondrial biogenesis, increases reactive oxygen species selectively only in cancer cells)
Ivermectin regulates tumor microenvironment (to inhibit tumor growth and progression, via P2X7 path, ICD - mediates immunogenic cell death)
Ivermectin inhibits cancer stem cells (which are responsible for tumor initiation, progression and recurrence)
Ivermectin inhibits tumor angiogenesis (tumor blood vessel creation)
Ivermectin has anti-mitotic activity (interacts with mammalian tubulin)
Ivermectin is an epigenetic regulator of cancer to inhibit cancer progression (alters gene expression to inhibit cancer progression, SIN3A, EMT)
Ivermectin can overcome tumor multidrug resistance
What cancers can Ivermectin treat?
The top 5 COVID-19 mRNA Vaccine Induced Turbo Cancers are: lymphomas, brain cancers, breast cancers, colon cancers and lung cancers (signals also seen in leukemias, hepatobiliary cancers, testicular cancers, sarcomas and melanomas)
Ivermectin has been shown to kill these cancer cells (in vitro or in vivo):
breast cancer, especially triple negative breast cancer which is often seen in COVID-19 mRNA Vaccinated women and has the worst prognosis.
glioblastoma and gliomas (glioblastomas are often seen in COVID-19 mRNA Vaccinated individuals)
leukemias, both AML and CML (these are the most aggressive and quickly lethal mRNA Turbo Cancers)
colorectal cancer (Stage 4 Colon cancers common in COVID-19 mRNA vaccinated)
hepatobiliary cancers: hepatocecullar carcinoma, cholangiocarcinoma, pancreatic cancer (major signal with COVID-19 mRNA Vaccines)
lung cancer (Stage 4 lung cancers in COVID-19 mRNA Vaccinated)
melanoma (definite signal in COVID-19 mRNA vaccinated)
renal cell cancer (possible signal with mRNA Turbo Cancers) and urothelial carcinoma
ovarian cancer (possible signal with mRNA Turbo Cancers)
prostate cancer (possible signal with mRNA Turbo Cancers)
There is almost no literature on Ivermectin and lymphomas which are probably the most common COVID-19 mRNA vaccine turbo cancers - this must be investigated.
What dose of Ivermectin to treat COVID-19 mRNA Vaccine Turbo Cancer?
Guzzo et al published a paper in 2022 on the “Safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of escalating high doses of Ivermectin in healthy adult subjects”
The highest dose tested to be safe with no side effects, was 2 mg/kg.
Max concentration in plasma is 4 hours after oral intake
Half life is 18 hours
Dr.David E. Scheim PhD, Blacksburg VA also wrote an interesting article on Ivermectin Safety in Sep.7, 2021 (Source)
Several studies have shown that Ivermectin’s anti-cancer effects are DOSE-DEPENDENT (higher dose = better response)
Warning: not to be taken as medical advice - hypothetical situation: if I was faced with a COVID-19 Vaccine Induced Turbo Cancer or an advanced stage cancer, I would be looking at an Ivermectin dose of 2mg/kg orally, daily or every two days.
Dr. Justus Hope MD published an article on Aug.29, 2023 that discusses anecdotal cases of Stage 4 Colon cancer, Stage 4 Ovarian Cancer responding to Ivermectin with dramatic drop in Tumor markers.
Also mentioned is a “High Dose Ivermectin” regimen of 2mg/kg per day for a doctor with Stage 4 Gallbladder cancer, taken for over a year, with visual side effects for a few days initially which resolved.
Also described is a case of enlarged Prostate suspicious for cancer, and a 5 week Ivermectin 45mg/day regimen that dropped PSA from 89.1 to 10.9 with resolution of nocturnal urinary frequency. For a 100kg man, that is a dose of 0.45mg/kg, significantly lower than the 2 mg/kg safe dose published by Guzzo et al.
The article describes a cancer patient with a neck tumor and lung metastases on a High Dose Ivermectin regimen of 2.45mg/kg daily.
I believe that it is a reasonable hypothesis that COVID-19 mRNA Vaccine Turbo Cancer patients could benefit from High Dose Ivermectin regimens, such as 2mg/kg and we urgently need more research to be done in this area.
(mRNA Vaccine Induced Turbo Cancers such as leukemias, glioblastomas, breast cancers (including triple negative), colon cancers, hepatobiliary cancers, lung cancers, melanomas, renal cell cancers, ovarian cancers, prostate cancers - as there is already evidence in the literature)
Do NOT comply.














No wonder they hate ivermectin so much
This information is extremely important and valuable. Thank you so much for gathering it and sharing it!