
Discover more from 2nd Smartest Guy in the World
Exposing Psyops & Scams
Over 36,000 subscribers
Already have an account? Sign in
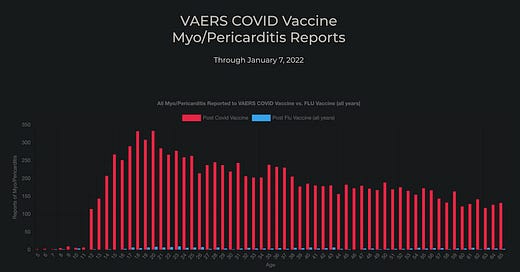
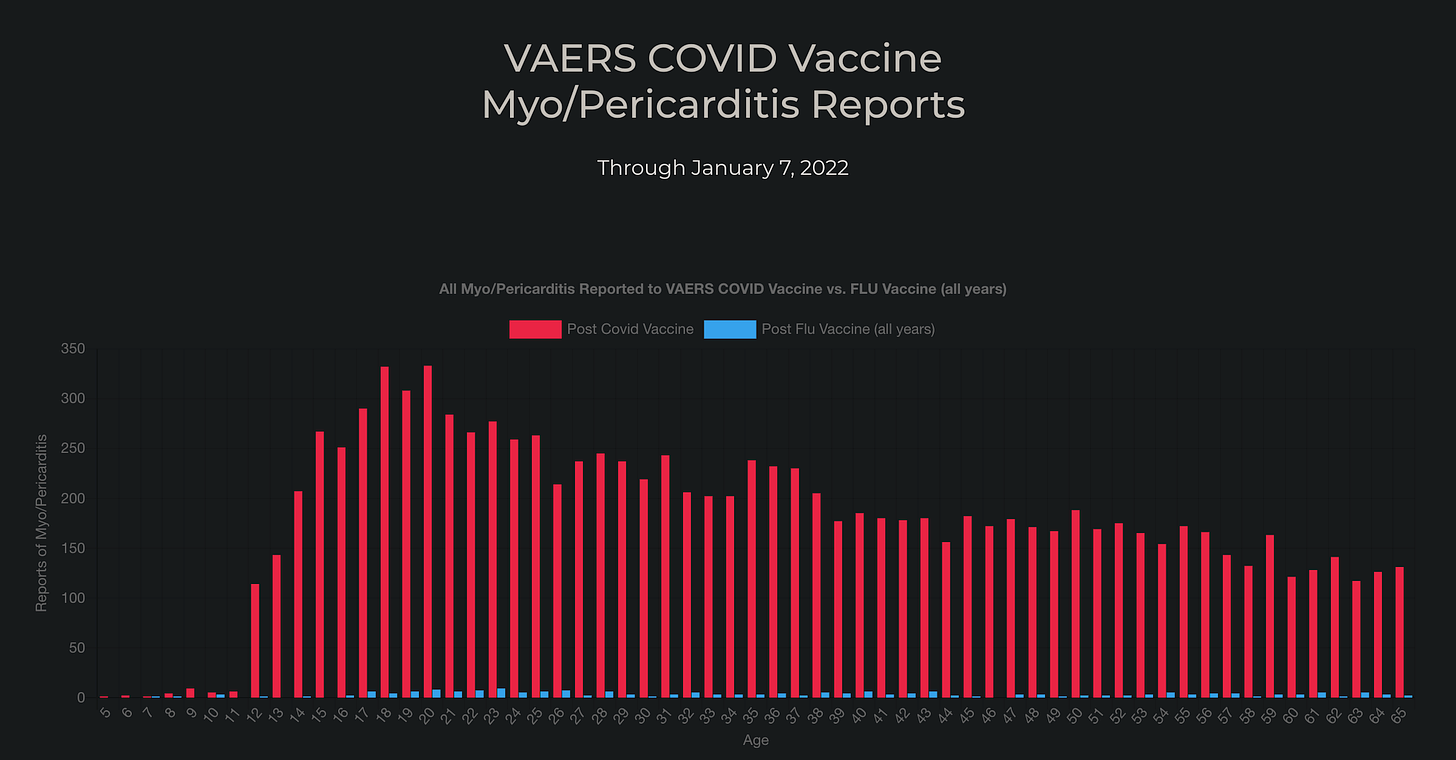
This may be of interest as a visual guide to Myo/Pericarditis cases post Death Injections roll out:
Source: VAERS COVID Vaccine Myo/Pericarditis
EDIT: The Underreporting Factor (URF) has been conservatively estimated at 41, though as per Harvard it’s likely more than double that.
Comply and YOU Die.
Subscribe to 2nd Smartest Guy in the World
Thousands of paid subscribers
Exposing Psyops & Scams







most useful thankyou.
i have a few relatives who dont think its a big deal, cos 'they were ok'
Here's another interesting thing about myocarditis. When the Death Cult Media started reporting it as a side effect they'd use the term along with it as "mild" or totally breeze by it, like myocarditis is merely a pimple on the nose. Errrr WRONG!!! When I heard the term myocarditis being put out more and more several months ago, I looked up the medical definition. It's not good to get and to be frank...if you are being rushed to an ER or collapse from it and are revived, your life expectancy outlook is not too good.
34
VII. PROGNOSIS
The prognosis for myocardidites is variable and depends on many factors:
etiology, histological and immunological characteristics, clinical pattern, and
presence of complications and possible use of artificial circulation methods.
We know that myocarditis often occurs without symptoms and ends with
complete recovery. A favorable prognosis is common for patients with acute or
fulminant course of the disease (in the case of successful correction of
hemodynamic instability). If the course is chronic, a considerable number of
patients (up to 21% within 3 years) develop dilatation cardiomyopathy, and in this
case, the prognosis depends on the presence of symptoms of chronic cardiac
insufficiency.
If cardiac rhythm disorders occur, the prognosis often depends on the
possibility of specific interventions, including implanting various devices.
The predictors of a poor prognosis include an increase in the QRS complex
over 120 msec, the presence of syncopal conditions, low systolic arterial pressure,
elevated pressure in the pulmonary artery and dysfunction of the right ventricle.
The risk of an unfavorable outcome increases if the immunohistochemical study is
positive and there are no beta-adrenoblockers in the comprehensive therapy.
Identification of the viral genome and a positive response for the Dallas criteria do
not affect the prognosis.
Despite aggressive therapy, almost 8% of the patients with lymphocytic and
over 50% of the patients with giant cell myocarditis require heart transplants. Here,
there is a sharp increase in the frequency of conductance disorders in the donor
heart and higher transplant rejection reaction frequency. In lymphocytic
myocarditis, the rejection risk rises 2-2.5 times; in giant cell active myocarditis it
develops in the transplanted heart in almost every fourth patient. The average
lifetime in giant cell myocarditis is 5.5 months from the time the first symptoms
appear.
35
The prognosis for specific myocardidites (diphtheria, sarcoidosis, Chagas’
diseases and others) depends on an early diagnosis and the start of pathogenetic
therapy
http://cardio-eur.asia/media/files/clinical_recommendations/2019_eng.pdf